To better serve honey import businesses, this article provides a comprehensive overview of China's current import requirements for honey, based on recent announcements issued by the GACC regarding inspection and quarantine requirements for imported honey from relevant countries. The coverage includes permitted honey varieties, production facility standards, inspection and quarantine protocols, production/storage/transportation specifications, certification prerequisites, packaging and labeling regulations, port inspections, and laboratory testing procedures. This guidance enables enterprises to fully understand regulatory requirements and ensure smooth product importation.
1. Permitted Honey Varieties
In accordance with the national mandatory standard "National Food Safety Standard - Honey" (GB 14963-2011) and the GACC's "Announcement on Inspection and Quarantine Requirements for Imported Honey from Rwanda" (Announcement No. 169 [2024]), among other documents, honey permitted for import into China refers to natural sweet substances produced by bees. These substances are created through the collection of plant nectar, secretions, or honeydew, which are then mixed with the bees' own secretions and fully fermented.


Figure 1 Honey
II. Manufacturer Requirements
Overseas manufacturers exporting honey to China must be registered with the General Administration of Customs of the People's Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as "the Chinese side"). The standard procedure is as follows: The competent authority of the exporting country or region shall evaluate the honey production facilities intended for export to China. Upon confirming compliance with Chinese laws, regulations, standards, and the requirements of the Protocol, they shall recommend these manufacturers to the Chinese side. Honey manufacturers that are not registered are prohibited from exporting honey to China.
III. Inspection and Quarantine Requirements
(I) Bees supplying raw materials for honey exports to China shall meet the following conditions:
1. Originate from apiaries located within the exporting country/region, which must be registered and effectively supervised by the competent authorities of said country/region.
2. The nectar, secretions, or honeydew collected by bees shall be safe and non-toxic, and must not originate from toxic nectar plants or genetically modified plants.
3. The exporting country/region shall confirm the absence of seven bee diseases listed in WOAH's "Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals" and other apian diseases within specified areas and timeframes.
(II) Per relevant GACC announcements, the following apian disease quarantine requirements shall apply:
1. Quarantine requirements for American foulbrood and European foulbrood.
The apiary and its surrounding area within a radius of 5 kilometers or 3 kilometers must be free from American foulbrood and European foulbrood for 12 months or 6 months prior to the export of the products to China.
2. Quarantine requirements for Varroa mite infestation in honey bees.
The apiary and its surrounding area within a 5-kilometer radius must be free from Varroa mite infestation for 12 months prior to the export of the honey to China. Alternatively, the honey must be filtered through a sieve with a pore size not exceeding 0.42 mm, heated to a core temperature of 50°C and maintained at this temperature for 20 minutes, or frozen to a core temperature of -12°C or lower and maintained at this temperature for at least 24 hours to ensure the elimination of Varroa mites and their eggs. Additionally, necessary measures must be taken to effectively remove mite residues and eggs.
3. Quarantine requirements for small hive beetle (Aethina tumida) infestation.
The honey in this batch originates from apiaries certified free of small hive beetle (Aethina tumida) infestation; or has been filtered through sieves with pore sizes not exceeding 0.42 mm; or has undergone heat treatment reaching a core temperature of 50°C maintained for 24 hours; or has been frozen to a core temperature of -12°C or below for at least 24 hours. These measures ensure the elimination of small hive beetles and their eggs, with additional procedures implemented to effectively remove any residual beetle fragments and eggs.
4. Quarantine requirements for Varroa destructor (Varroa mite).
This batch of honey is sourced from apiaries located in regions with no reported cases of Varroa destructor infestation; or has been filtered through sieves with pore sizes smaller than 0.42 mm; or has been processed at a core temperature exceeding 50°C for a minimum of 20 minutes or at a core temperature of -12°C or lower for at least 24 hours to ensure complete eradication of Varroa mites, accompanied by necessary measures to effectively eliminate mite residues.
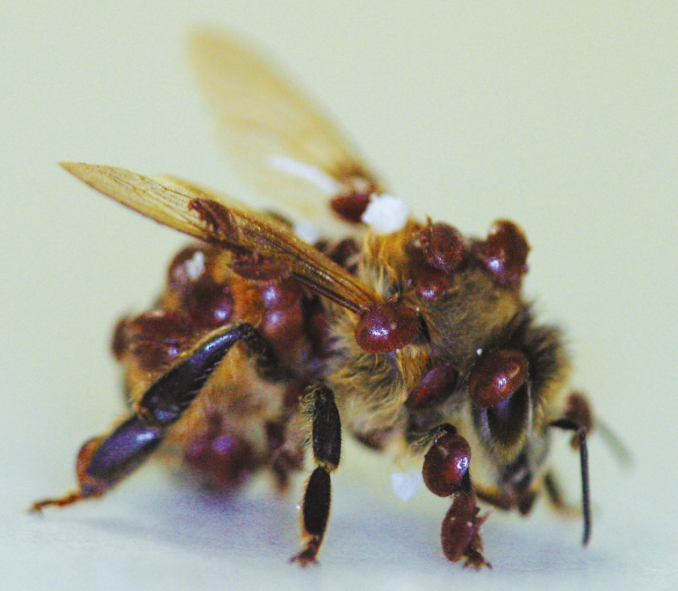
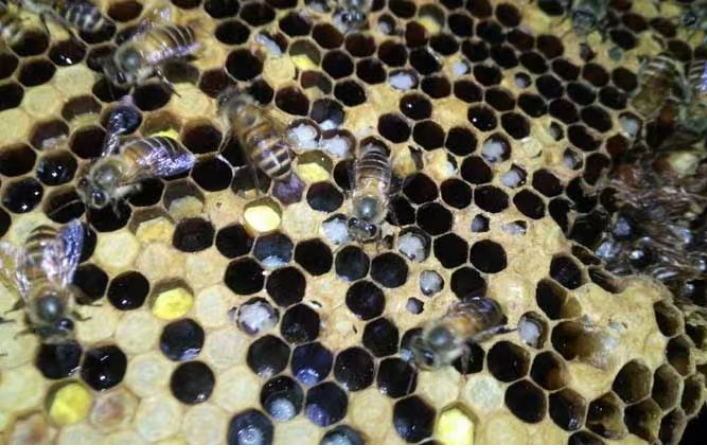


Figure 2 Bee mite infestation and American foulbrood
IV. Production, Storage, and Transportation Specifications
(I) The apiaries supplying raw materials for honey production destined for China have never utilized veterinary drugs prohibited by either China or the exporting countries/regions.
(II) Honey exported to China originates from processing enterprises with established traceability systems, ensuring full traceability back to the source apiaries.
(III) Residue levels of veterinary drugs, pesticides, microorganisms, heavy metals, and other environmental contaminants in honey exported to China shall not exceed the maximum limits established by China or the exporting countries/regions.
(IV) During major public health emergencies, enterprises shall implement epidemic prevention measures in compliance with international standards, establish necessary honey safety protocols, and ensure effective contamination prevention throughout the entire supply chain - from raw material reception to processing, packaging, storage, and transportation.
(V) Honey products exported to China meet all hygiene and safety standards for human consumption.
(VI) Throughout the entire process of processing, storage, and transportation of honey exported to China, it must comply with the relevant hygiene standards of both China and the exporting country or region to prevent contamination by toxic or hazardous substances. Honey exported to China shall not be processed or mixed with products that fail to meet the requirements of the Protocol, products from non-registered processing facilities, or other products from the same registered processing facility.
(VII) The exporting country or region shall ensure proper labeling at all stages, from apiaries to processing, packaging, and storage. A dedicated storage area or independent warehouse for honey exported to China must be established and clearly marked.
(VIII) After the goods are loaded into containers, they shall be sealed under the supervision of officials from the exporting country or region. The seal number must be recorded in the veterinary health certificate (Note: Cuba does not require sealing). Packaging must not be opened or replaced during transportation.
V. Certification Requirements
(I) Each container/batch of honey exported to China shall be accompanied by at least one original health certificate, certifying that the products comply with the veterinary and public health laws and regulations of both China and the exporting country or region, as well as the relevant provisions of the bilateral protocol.
(II) The format, language, and content of the veterinary health certificate must be mutually agreed upon by both parties in advance.
(III) If required, the exporting country or region shall provide the Chinese side with the following for filing: inspection and quarantine seal impressions, sample health certificates, a list of authorized signatories with corresponding signature specimens, and descriptions of anti-counterfeiting measures. Any modifications must be communicated to the Chinese side in advance.
VI. Packaging and Labeling Requirements
(I) Honey exported to China must be packaged using food-contact materials that comply with China's national food safety standards.
(II) The packaging must be sealed and labeled in Chinese with the following information: product name, specifications, place of origin (specified to state/province/city), manufacturer registration number, production batch number, destination (must be clearly marked as the People's Republic of China), manufacturing date (YYYY/MM/DD), and shelf life.
VII. Port Inspection
(I) Verify whether the quarantine certificate meets the requirements of the bilateral quarantine agreement.
(II) Verify that the product name, variety, specifications, quantity (weight), origin, packaging, and markings match the accompanying documentation.
(III) Inspect whether the product packaging marks and labels comply with regulatory requirements.
(IV) If laboratory testing is required, collect samples on-site and submit them for analysis.
Figure 3 Customs officers inspecting labels on imported and exported honey
VIII. Laboratory Testing
(I) Bee disease testing
The laboratory performs bee disease testing on honey from various countries in accordance with the annual National Port Safety Monitoring Plan and relevant control measures issued by the GACC.
(II) Other Inspections
In accordance with standards such as the "National Food Safety Standard - Honey" (GB 14963-2011), imported honey undergoes laboratory testing for sensory evaluation, physicochemical properties, contaminants, pesticide and veterinary drug residues, as well as microbiological indicators.
Key Takeaways
(I) Given the unpredictable nature of animal epidemic diseases, enterprises importing honey should first familiarize themselves with China's relevant quarantine regulations and the latest customs advisories. Prior to importation, comprehensive research should be conducted on the exporting country/region regarding bee disease prevalence, production processes, storage/transportation conditions, and packaging/labeling standards. Import agreements should only be finalized upon completing these assessments.
(II) Importing enterprises must prioritize compliance with inspection and quarantine requirements including port examinations, product labeling verification, and laboratory testing protocols. Full cooperation with customs authorities is required for quarantine inspections and sampling procedures. This helps prevent financial losses resulting from documentation discrepancies, failed on-site inspections, or non-compliant laboratory test results.
Disclaimer:The above content is translated from Chinese version of Shenzhen 95198. The Shenzhen 95198 version shall prevail.
Hot News